Windows 11 Windows 10 Windows 8.1 Windows 7
Microsoft Defender Offline is a powerful offline scanning tool that runs from a trusted environment, without starting your operating system.
When should I use Microsoft Defender Offline? #
Run Microsoft Defender Offline if:
- Windows Security (also called Windows Defender Security Center in previous versions of Windows) detects rootkits or other highly persistent malware on your PC and recommends you use Microsoft Defender Offline.
- You suspect your PC might have malware hiding on it, but your security software doesn’t detect anything.
How do I use Microsoft Defender Offline #
- Save any open files and close all apps and programs.
- Select Start , and then select Settings > Update & Security > Windows Security > Virus & threat protection .
- On the Virus & threat protection screen, do one of the following:
- In an up-to-date version of Windows 10 or Windows 11: Under Current threats, select Scan options.
- In older versions of Windows 10: Under Threat history, select Run a new advanced scan.
- Select Microsoft Defender Offline scan, and then select Scan now.
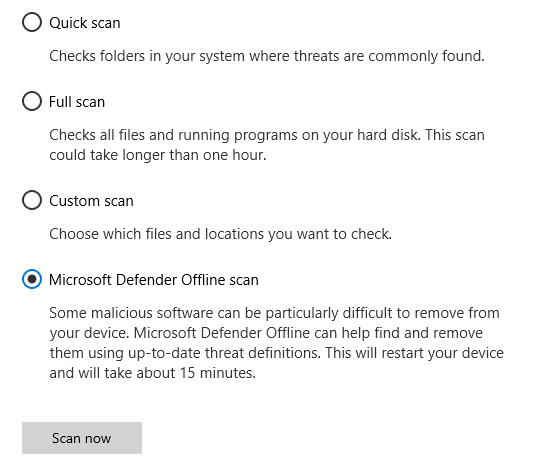
You’ll be prompted that you’re about to be signed out of Windows. After you are, your PC should restart. Microsoft Defender Offline will load and perform a quick scan of your PC in the recovery environment. When the scan has finished (usually takes about 15 minutes), your PC will automatically restart.
Notes:
- You typically need administrator rights on the PC on which you plan to run Microsoft Defender Offline.
- If you experience a Stop error on a blue screen when you run the offline scan, restart your device and try running a Microsoft Defender Offline scan again. If the blue-screen error happens again, contact Microsoft Support.
Where can I find scan results? #
To see the Microsoft Defender Offline scan results:
- Select Start , and then select Settings > Update & Security > Windows Security > Virus & threat protection .
- On the Virus & threat protection screen in Windows 10, under Current threats, select Scan options, and then select Protection history (In previous versions of Windows it may say Threat history).
